Two kinds of analyses are presented in this section: (1)analysis of characteristics of entries in the multicast routing tables, mroutes; and (2)analysis of characteristics of multicast traffic passing through the routers that we collect data from. For a more extensive analysis of multicast routing tables at FIXW-MBONE (fixw-mbone.nsn.nasa.gov) please refer to Bill Fenner's work. Following is a list of graphs available in this section. List of Available Graphs: More Info:
What is a multicast routing table and what is an "mroute" ? Multicast routers maintain state about the incoming and outgoing interfaces for each (S,G) pair --source-group pair. This state is used to decide which packets are to be discarded and which are to be forwarded. The table that router maintains for holding this state information is called multicast routing table. Each entry in this table corresponds to a unique (S,G) and is referred to as mroute. Each mroute primarily contains 4 types of entries: (1)address of the multicast group; (2)address of the corresponding source (or * for all sources); (3)incoming interface; and (4)list of outgoing interfaces. A hypothetical example: Lets us consider the example of a router that has three interfaces say, Inter-A, Inter-B and Inter-C . Now, consider a scenario where this router has an mroute entry for (S1, G1); i.e. source, S1 and group, G1; such that Inter-A is listed as an incoming-interface and Inter-C is listed as an outgoing-interface. With this entry in its multicast routing table if router receives a packet for (S1, G1) from Inter-A it will forward it to Inter-C. However, if packet is received from any other interface, it will discarded. go top
|

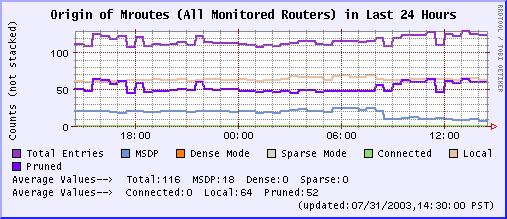 Last 24 Hours
Last 24 Hours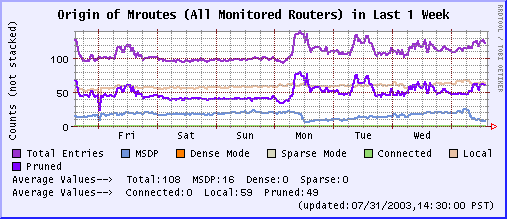 Last 1 Week
Last 1 Week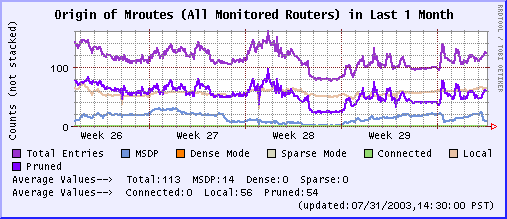 Last 1 Month
Last 1 Month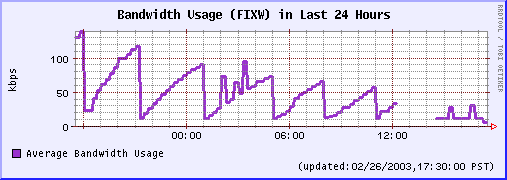 Last 24 Hours
Last 24 Hours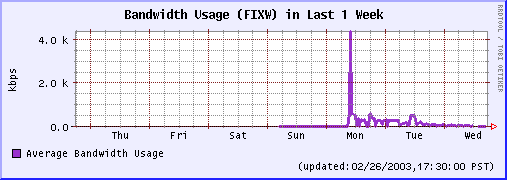 Last 1 Week
Last 1 Week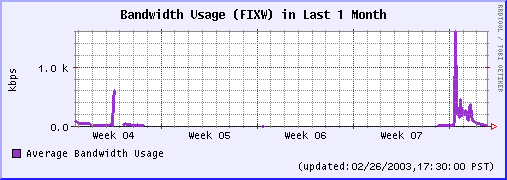 Last 1 Month
Last 1 Month